

This was a large study involving more than 7 million people. It was carried out by researchers from seven European institutions, led by the University of Milan. "Ibuprofen could raise the risk of heart failure by up to 83%," claims the Daily Mirror. But this headline massively overstates the danger of this painkiller.
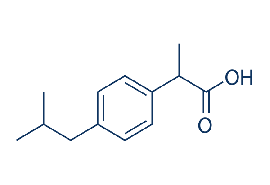
In fact, new research suggests that taking painkillers known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – which includes ibuprofen – increases the risk of heart failure by less than 20% overall.
NSAIDs are a group of painkilling medicines commonly taken by people with joint problems, backache and arthritis. They are prescribed to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
The study found that the risk of heart failure varies between NSAIDs and according to dosage.
While a rarely prescribed NSAID called ketorolac almost doubled the risk of heart problems, the more commonly taken ibuprofen increased the chance of heart problems by just 18%.
The risk was also highest for people who took an NSAID on a daily basis and in very high doses.
Some NSAIDs, such as ketoprofen and celecoxib, did not seem to increase the risk at all at usual doses.
This latest study backs up previous evidence that NSAIDs are clearly linked with an increased risk of heart failure. But it's important to bear in mind that the risk is, for most people, still very small.
Heart failure is caused by a wide range of conditions, including high blood pressure, heart attacks and obesity.